
Course Description: Atomic Structure
This concise course provides a fundamental understanding of the atom, the basic building block of matter. Students will explore the historical development of atomic theory, from early philosophical ideas to modern quantum mechanical models.
Key Topics Covered
The course focuses on the internal organization and properties of the atom, including:
Subatomic Particles: Identification and characteristics of protons (positive charge, found in the nucleus), neutrons (no charge, found in the nucleus), and electrons (negative charge, orbiting the nucleus in shells/orbitals).
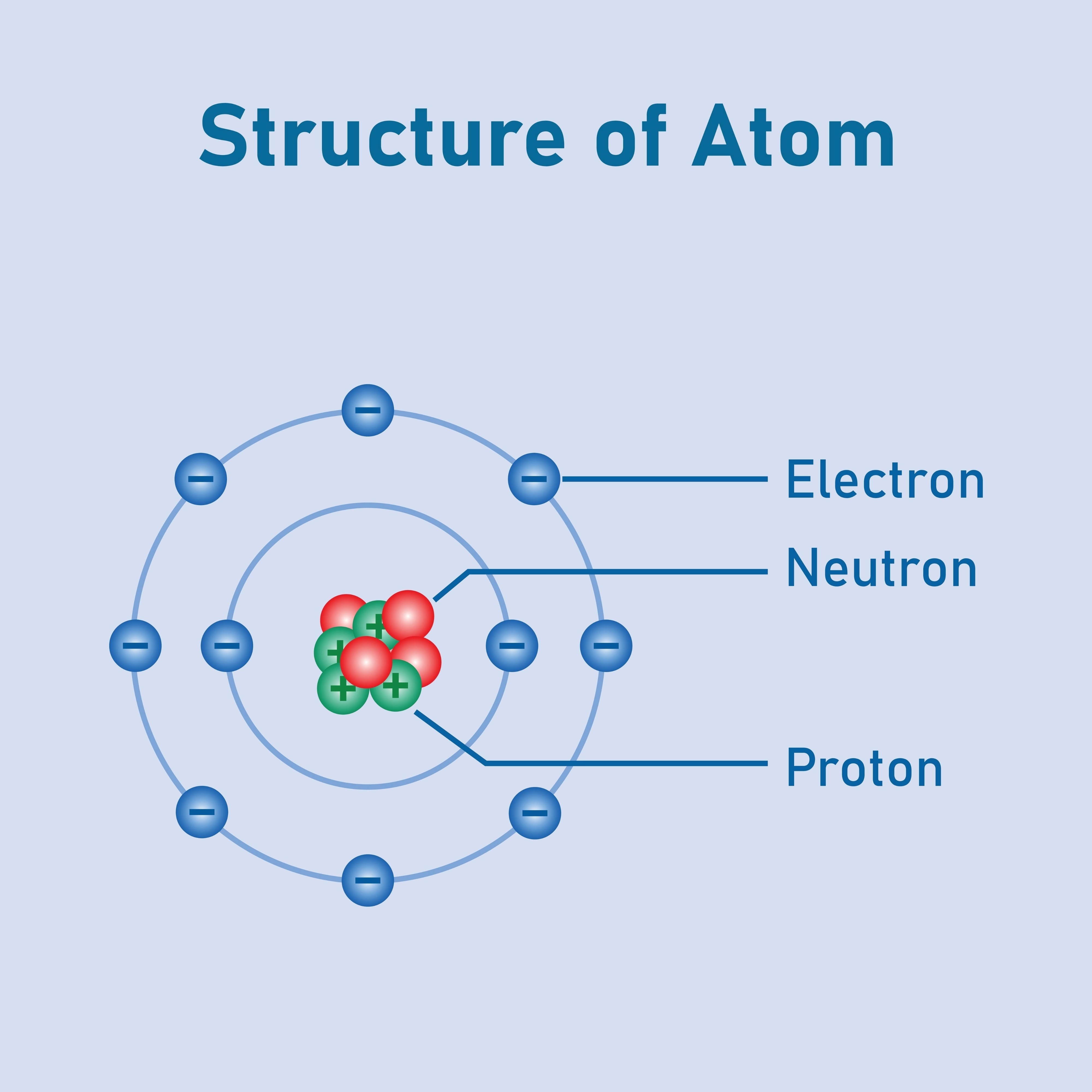
Atomic Definitions: Understanding key terms like Atomic Number (Z) (number of protons), Mass Number (A) (protons + neutrons), and the concept of Isotopes (atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons).
Historical Models: A review of influential atomic models, such as Dalton's, Thomson's (Plum Pudding), Rutherford's (Nuclear Model), and Bohr's model, highlighting how scientific understanding evolved.
Electron Configuration & Quantum Mechanics: Introduction to the modern Quantum Mechanical Model, including electron shells (energy levels), subshells (s, p, d, f), orbitals, and the rules governing how electrons fill these energy levels (Aufbau principle, Hund's rule, Pauli exclusion principle).
Periodic Trends: Analyzing how atomic structure dictates the organization of the Periodic Table and influences periodic properties like atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity
Ions and Stability: Explaining how atoms gain or lose electrons to form ions and achieve stable electronic configurations, which is foundational to understanding chemical bonding.
- Teacher: Admin User